

One of the often overlooked elements of the localization workflow is file management. Sending files back and forth between all parties involved in the localization process can become an error-prone and time-consuming task if not done with the right tools.
This is especially relevant in the case of software localization and its ever-growing list of programming languages and file formats. Most of the file formats used in software development aren’t human readable and linguists don’t normally work directly on them, as they would risk breaking the code because of an incorrectly placed translation.
Hence, one of the most important steps of the localization workflow consists of extracting the translatable content from the software’s code and converting it into a format that linguists can easily work with.
An XLIFF file is an XML-based file format which is used as the interchange format for any Computer-aided translation software, commonly referred to as CAT tools. This file format contains translatable text in the original language and the language in which it needs to be translated into. In localization, these are known as source and target language. Nowadays, most linguists work with XLIFF because they can translate while viewing the text in both the source and the target language, as well as use the content previously stored on translation memories [^definition] and glossaries.
At this point you might be wondering, how do linguists obtain an XLIFF file out of an XML, JSON or .strings file?
If the localization is carried out by a translation agency, this responsibility normally falls on the localization engineer who, in addition to converting the file, also makes sure that at the end of the workflow the translated content is converted back to its original format and that its structure is left intact.
In the case of freelance linguists, nowadays many CAT tools in the market offer file conversion and import functionalities. However, these can be quite difficult to use, so most linguists will ask their clients to send them an XLIFF or another file format that can be easily converted with a CAT tool.
With this in mind, Applanga offers an all-in-one solution that allows developers to integrate their app content with our cloud-based localization management platform where, in turn, linguists and testers can complete their tasks on a simple, user-friendly interface. This way, for those who want to automate their localization workflow as much as possible, file conversion and management is also taken out of the equation.
Applanga supports a wide range of file formats. Whether you upload your app’s content manually or via one of our existing integrations, Applanga will extract the translatable content from your files and make it accessible to linguists through our platform.
You and your team of translators, reviewers and testers can then manage the localization workflow and carry out linguistic tasks on our editor view, which shares many of the functionalities found in a CAT tool.
Alternatively, if you prefer to use TransPerfect Translations Services, you can send content for translation from Applanga to GlobalLink Project Director via an integration that will use XLIFF files as exchange file format.
What’s more, if you uploaded screenshots to your Applanga project, these auto-generated XLIFF will include links to screenshots in its structure. This way, linguists can use them as reference with the preview function in TransPerfect’s CAT tools.
Any user who is added to Applanga can manually export or import content into Applanga at any point of the localization process in any of the following formats: .csv, .tsv, .ini, .js, .json, .properties, .po, .pot, .resw, .resx, .strings, .stringsdict, .xls, .xlsx, .xliff, .xlf, .xml, .yaml, .yml, .arb, .tmx, .tbx, .php.
This way you can effectively convert your files into XLIFF by using a combination of these two features.
You can convert your Android XML files into XLIFF by following these simple steps:
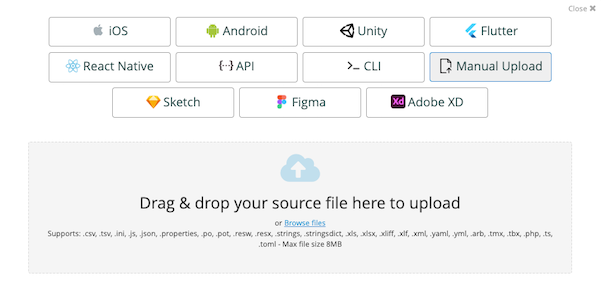
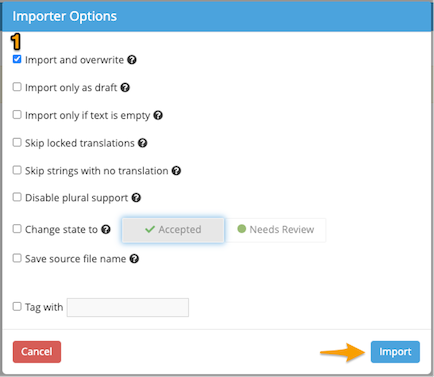
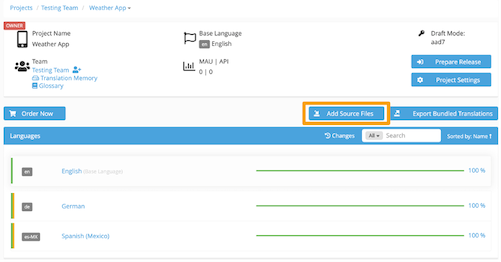
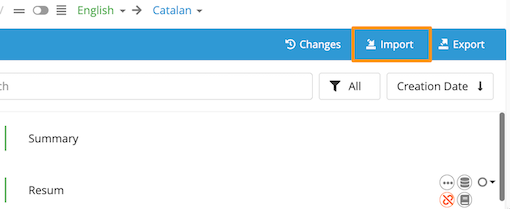
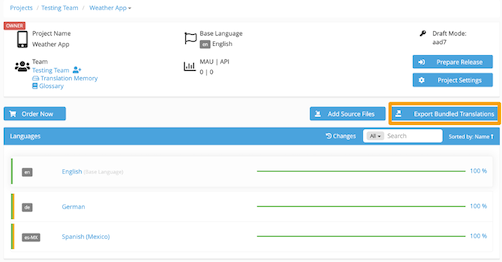
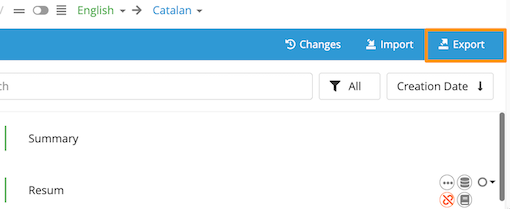
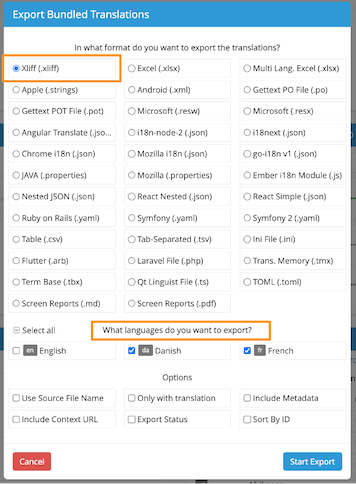
The steps to convert an Excel file into an XLIFF in Applanga are almost identical. The only difference lies in that there is an additional step during the import process.
After you upload the Excel file to Applanga and select the applicable importer options, you will be redirected to an Import Spreadsheet pop-up where you will need to label each column header of your Excel file using the available options on the drop-down menu.
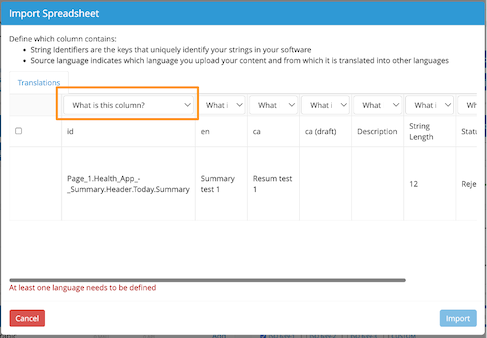
Once this is done, simply click on Import.
A guide for using Over-the-Air updates and pluralization with React-Native and Applanga
Read the Full ArticleAre you wondering which keys stored in your Applanga projects are actually used in your app and which ones are just dead weight?
Read the Full Article