Learn how GL Strings supports non-standard characters
GL Strings supports characters that go beyond those commonly used in the English basic alphabet and punctuation marks, enabling representation of diverse languages. Any Unicode character can be entered into the GL Strings editor.
While the GL Strings editor accepts any Unicode character, how the string ultimately appears to the end users depends on several downstream factors:
Font Support:
Not all fonts support every glyph required to visually represent a character. If the font does not include a particular glyph, it may not display correctly and instead show a placeholder, such as a square (□) or a question mark (?).
Encoding and Integration:
When integrating localized strings into source code, design files, or content management systems, it’s essential to ensure proper character encoding (such as UTF-8). Inconsistent encoding or integration errors can can lead to character corruption or rendering issues.
Environment Differences:
Local testing (development environment), staging, and production environments can produce different results due to differences in server configuration, caching, or deployment processes. The final production environment is the only true indicator of end-user experience.
Font Availability = Glyph Rendering:
Characters will only display correctly if the necessary font and its glyph, is available and properly applied, whether in a design tool like Figma (font installed locally or accessed via Figma’s limited cloud library) or in a website/app (font included and referenced in code or style sheet).
Test localized strings in their final destination environment to ensure the strings display correctly. This step is important, especially for languages that use less common scripts or symbols.
You can directly enter the Unicode character using a virtual keyboard or the keyboard shortcut, or copy and paste the character into the GL Strings editor.
Helpful external resources:
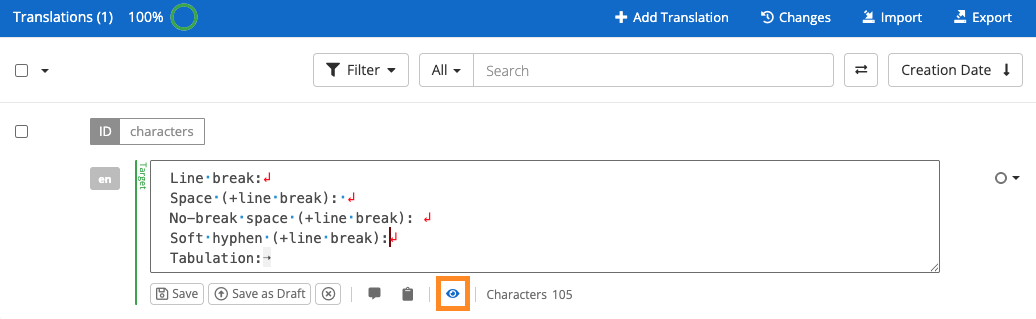
Non-printable characters, also known as formatting marks or hidden characters, are used for content design in text files or user interfaces and aren’t displayed at printing or in the rendered UI. Some of the most common ones are line breaks, spaces, non-breaking spaces, tabulators and soft hyphens.
The editor view supports non-printable unicode characters, but not all of them are visible by default. In this article, we’ll explain the different ways in which they are displayed on the editor view.
📝 Note: This functionality is exclusively available on the Chrome web browser.
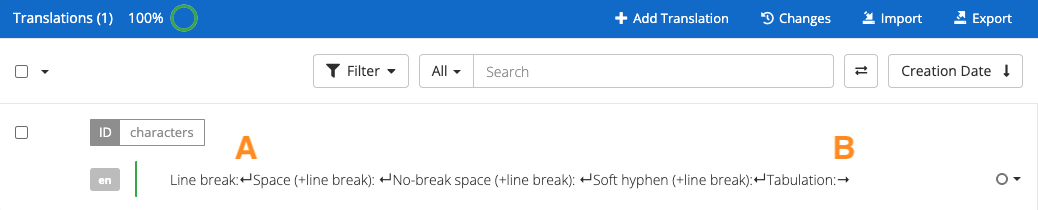
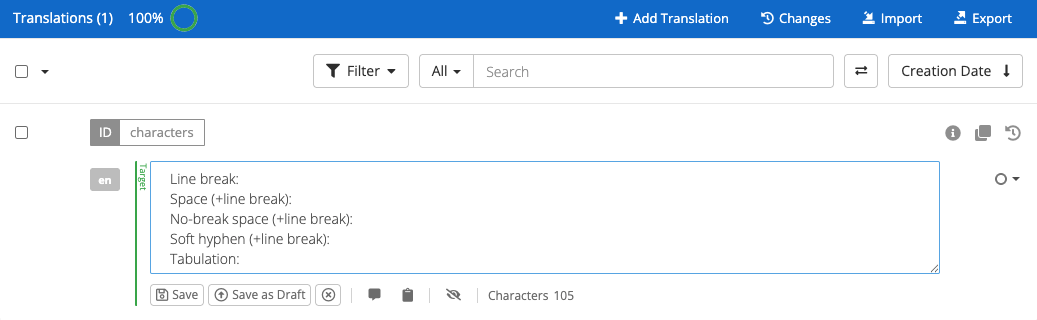
| Hidden character | Representation | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Line break | red return symbol | |
| Space | blue dot | |
| No-break space | space | This includes leading and trailing spaces |
| Soft hyphen | purple pipe symbol | |
| Tabulation (tab) | right arrow |